1. Introduction
In today’s fast-paced financial landscape, data security is one of the most critical challenges for fintech companies. As digital transactions, mobile banking, and online investment platforms grow in popularity, so does the volume of sensitive data being processed and stored. This makes fintech applications a prime target for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for fraud, identity theft, and financial gain.
Traditional security systems, while effective to a point, often struggle to keep up with the sophistication of modern cyber threats. This is where blockchain technology emerges as a game-changing solution. Known for its decentralized architecture, immutability, and cryptographic security, blockchain offers a robust framework for protecting financial data from unauthorized access and tampering.
By enabling transparent, tamper-proof, and verifiable transactions, blockchain not only strengthens security but also fosters trust between fintech providers and their customers. In this article, we explore how blockchain enhances data security in fintech applications, the challenges it addresses, real-world use cases, and the future trends shaping this powerful synergy.
2. Understanding Blockchain in the Context of Fintech
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof manner. Unlike traditional databases, which are controlled by a central authority, blockchain stores data across a network of nodes. Each transaction is encrypted, grouped into a “block,” and linked chronologically to previous blocks, forming an immutable chain.
In the fintech (financial technology) sector, blockchain is emerging as a game-changer for data security, transparency, and operational efficiency. Fintech applications—ranging from mobile banking to cryptocurrency exchanges—require handling vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, transaction records, and financial assets. Blockchain’s cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms ensure that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without network-wide approval, drastically reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized changes.
There are three main types of blockchain relevant to fintech:
- Public Blockchains (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) – fully decentralized, ideal for open financial networks.
- Private Blockchains – permissioned systems controlled by a single entity, suitable for internal banking operations.
- Consortium Blockchains – semi-decentralized, governed by a group of organizations, common in interbank transactions.
By combining decentralization, encryption, and transparency, blockchain enables fintech companies to build more secure, auditable, and trust-driven applications, helping them meet both customer expectations and regulatory compliance requirements. This makes blockchain a powerful ally in the ongoing evolution of secure financial services.
3. Key Data Security Challenges in Fintech
The fintech sector deals with highly sensitive financial and personal data, making it a prime target for cybercriminals. As digital transactions grow, so do the risks. Key data security challenges include:
Cyberattacks and Hacking Incidents
Fintech platforms face constant threats from hackers seeking to exploit vulnerabilities. Attacks such as phishing, malware injection, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) can disrupt operations, compromise accounts, and steal financial data.
Fraudulent Transactions and Identity Theft
Online payment systems, digital wallets, and peer-to-peer transfers are susceptible to fraudulent activities. Cybercriminals often use stolen credentials to authorize illegal transactions or create fake accounts for money laundering.
Insider Threats and Data Manipulation
Employees or contractors with access to sensitive systems may intentionally or unintentionally cause security breaches. Insider threats are especially dangerous because they bypass traditional security measures.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy
Fintech companies must comply with strict regulations such as GDPR, PCI DSS, and AML/KYC requirements. Failure to protect data adequately can result in heavy fines, reputational damage, and legal action.
Vulnerabilities in Third-Party Integrations
Many fintech applications rely on APIs and third-party services for payment processing, authentication, or analytics. Weaknesses in these integrations can expose the platform to cyber risks.
Real-Time Data Processing Risks
Fintech platforms require instant transaction verification, making them vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks or real-time fraud attempts if communication channels are not fully secured.
These challenges highlight the urgent need for advanced, tamper-proof security frameworks. Blockchain’s immutable ledger, encryption, and decentralized structure offer strong solutions to address these threats, making it a natural fit for enhancing data security in fintech applications.
4. How Blockchain Improves Data Security in Fintech Applications
Blockchain offers a robust framework for strengthening data security in fintech applications by addressing vulnerabilities that traditional centralized systems struggle to manage. Its decentralized, transparent, and cryptographically secure architecture delivers multiple layers of protection.
Immutable Ledger
Once a transaction or data entry is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from the network. This immutability makes it nearly impossible for malicious actors to manipulate transaction histories, reducing fraud risks.
Encryption and Cryptographic Signatures
Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions. Every transaction is digitally signed using public-private key pairs, ensuring authenticity and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive financial data.
Decentralization to Remove Single Points of Failure
Unlike centralized databases that store all information in one location, blockchain distributes data across multiple nodes. This eliminates single points of failure, making it much harder for hackers to compromise the entire system.
Smart Contracts for Secure Automation
Smart contracts enable automated, rule-based transactions without intermediaries. This reduces human error, enhances trust, and prevents unauthorized interference in payment processes, lending, and other financial activities.
Real-Time Auditability
Blockchain’s transparent ledger allows for real-time tracking and auditing of transactions. Regulators, auditors, and internal compliance teams can instantly verify records, making it easier to detect suspicious activities.
Enhanced Identity Verification
Blockchain can securely store and verify digital identities, helping fintech companies meet KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) requirements without exposing sensitive personal information to unnecessary risks.
By combining these features, blockchain not only enhances fintech security but also builds greater trust with customers, regulators, and partners—positioning it as a critical technology for the future of financial services.
5. Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain in Fintech Security
Blockchain is already making a significant impact on fintech security, with practical applications across payments, identity management, and compliance.
Secure Cross-Border Payments
Traditional cross-border transfers can be slow, costly, and prone to fraud. Blockchain-based payment networks like Ripple and Stellar enable near-instant, low-cost international transfers while ensuring each transaction is encrypted, immutable, and traceable, reducing the risk of tampering.
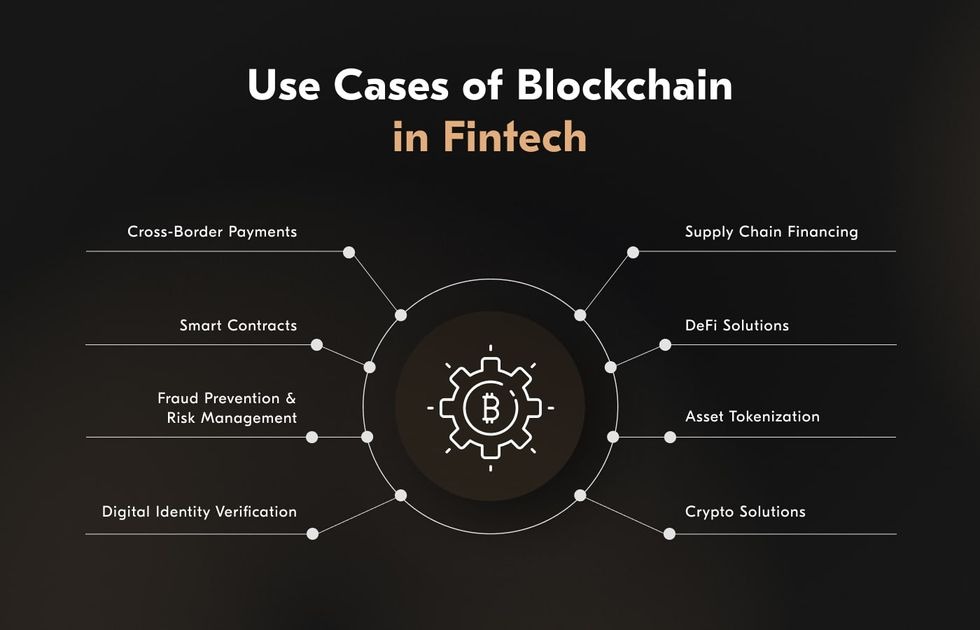
Fraud Prevention in Digital Banking
Banks and neobanks are leveraging blockchain to secure transaction histories and prevent unauthorized changes. By using immutable ledgers, suspicious activities can be flagged and investigated in real time, preventing large-scale fraud.
Identity Verification and KYC/AML Compliance
Fintech companies use blockchain-based digital identity platforms to securely store and share verified customer information. This helps meet Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements while minimizing the risk of identity theft. Solutions like Civic and SelfKey give users control over their personal data while providing verifiable credentials to service providers.
Secure Trading Platforms and Asset Tokenization
Blockchain enables secure and transparent trading of digital assets, stocks, and tokenized securities. Platforms like tZERO use blockchain to ensure transparent trade settlements, while tokenization allows fractional ownership of assets without compromising security.
Smart Contract-Based Lending
Peer-to-peer lending platforms integrate smart contracts to automatically execute loan agreements, ensuring terms are met without the risk of manual interference or data manipulation.
These real-world implementations show that blockchain is not just a theoretical solution—it is actively protecting transactions, identities, and assets in the fintech sector. As adoption grows, these use cases will expand, setting new security standards for the financial industry.
6. Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
While blockchain offers strong security advantages for fintech, its implementation is not without challenges. Businesses must address several technical, regulatory, and operational factors to ensure a smooth and effective rollout.
Scalability and Transaction Speed
Public blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin can experience network congestion, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees. Fintech applications handling high transaction volumes may require layer-2 scaling solutions or private blockchain networks to maintain speed and efficiency.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many financial institutions rely on complex legacy infrastructure. Integrating blockchain with these systems can be technically challenging, requiring custom APIs, middleware, and thorough testing to avoid operational disruptions.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Blockchain regulations vary widely across jurisdictions. Fintech companies must navigate complex legal landscapes, ensuring compliance with KYC, AML, GDPR, and financial licensing requirements. Regulatory clarity is still evolving, which can delay adoption.
Data Privacy Concerns
While blockchain provides transparency, storing personal data on an immutable ledger can conflict with privacy regulations, such as the right to be forgotten under GDPR. Careful design is needed to balance transparency with privacy.
Implementation Costs
Building and deploying blockchain solutions involves significant upfront investment in infrastructure, developer expertise, and ongoing maintenance, which can be a barrier for smaller fintech startups.
Skill Gaps
Blockchain expertise, particularly in the fintech context, is still limited. Companies may face difficulties finding developers skilled in both blockchain technologies and financial regulations.
Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, collaboration with regulators, investment in skilled talent, and careful technology selection to ensure that blockchain delivers its full security potential in fintech applications.
7. Future Trends in Blockchain-Based Fintech Security
The role of blockchain in fintech security is set to grow significantly as both technology and regulatory frameworks mature. Several emerging trends are shaping the future landscape:
AI-Driven Fraud Detection
The integration of artificial intelligence with blockchain will enable advanced fraud detection and risk assessment. AI can analyze blockchain transaction patterns in real time, identifying anomalies and preventing fraudulent activities before they occur.
Blockchain and Biometric Authentication
Combining blockchain’s immutable ledger with biometric verification methods—such as fingerprint, iris, or facial recognition—will strengthen identity security for fintech applications, reducing identity theft and unauthorized account access.
Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Security Protocols
As DeFi platforms gain popularity, new blockchain-based security protocols will emerge to protect users from exploits, flash loan attacks, and smart contract vulnerabilities, making decentralized financial services safer.
Increased Regulatory Clarity
Governments and financial authorities are developing clearer regulations for blockchain-based financial services. This will encourage greater adoption by providing legal certainty, especially for cross-border transactions and digital asset management.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
With the advancement of quantum computing, fintech companies will adopt blockchain platforms using quantum-resistant encryption to safeguard data against future threats.
Sustainable Blockchain Solutions
Energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) and hybrid models, will make blockchain more eco-friendly, aligning fintech security practices with sustainability goals.
These trends suggest that blockchain will not only remain a cornerstone of fintech security but also evolve to address future technological, environmental, and regulatory challenges—paving the way for safer, smarter, and more trusted financial ecosystems.
8. Conclusion
Blockchain is redefining data security in fintech by offering an immutable, decentralized, and cryptographically secure framework for managing financial transactions and sensitive data. From preventing fraud to enabling secure identity verification and ensuring regulatory compliance, blockchain provides solutions to many of the sector’s most pressing security challenges.
While implementation requires overcoming hurdles like scalability, integration with legacy systems, and regulatory complexity, the long-term benefits are substantial. As emerging trends—such as AI-driven fraud detection, biometric authentication, and quantum-resistant cryptography—gain traction, blockchain’s role in fintech security will only strengthen.
Fintech companies that adopt blockchain early will not only enhance their security posture but also gain a competitive edge in building trust with customers and regulators. In a rapidly evolving financial landscape, blockchain stands out as a foundational technology for creating secure, transparent, and resilient digital financial systems.



